Search
Results for 'forms'
Clear-
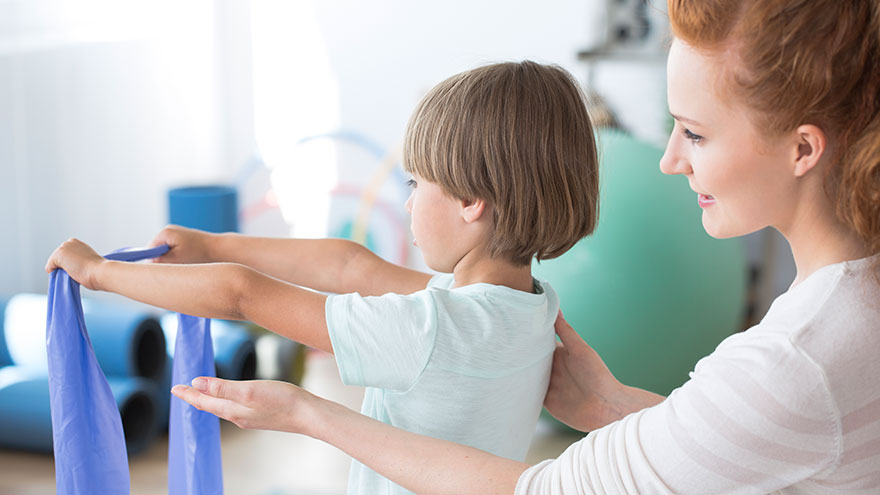
Ask the Expert: What is Scoliosis?
Posture is important, but for those children diagnosed with scoliosis (spinal curvature) it can be a difficult issue. The Washoe County School District Student Health Services Department screens 7th grade students for scoliosis as growth spurts often reveal the condition and, if diagnosed early, scoliosis can stop progressing. We asked Michael Elliott, MD, head of the Department of Pediatric Orthopedics and Scoliosis to answer some frequently asked questions about scoliosis. What is scoliosis? There are many types of scoliosis: early onset (occurs before age 10), congenital scoliosis is when the bones of the spine do not form correctly, neuromuscular scoliosis which is due to children’s neurologic and muscle disease, and the most common is Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis. The term “idiopathic “ means the exact cause is unknown, although we do know it runs in families. This type of scoliosis occurs in 2-3 percent of adolescents and is mainly seen during their growth spurt. This is why middle school screenings are recommended. Both genders get scoliosis but girls are 8 times more likely to have their curves progress and become larger. What are the signs that my child may have scoliosis? A few signs for parents to watch for are: One shoulder might be higher than the other. One leg may seem longer. A hip may be higher or look more prominent. The waist may not look the same from side to side (asymmetry). The trunk or rib cage may be more prominent on one side or shifted. When they bend forward they may have a bump on their back. How is scoliosis diagnosed? It can be noticed by a pediatrician at a physical, school screening nurse, PE teacher or parents. Once the curve is suspected the child is usually referred to a pediatric orthopedic surgeon scoliosis expertise. At the initial visit the doctor will perform a thorough physical including a complete neurologic exam to assess the amount of curvature. Once the exam is completed the physician will determine if a spinal x-ray is needed. The curve on the x-ray is measured utilizing the cobb angle (a measurement in degrees) which helps guide the treatment. What are common treatments for scoliosis? The treatment depends on the size of the spinal curve and the amount of growth the child has remaining. An x-ray of the child’s hand is used to determine the amount of growth remaining. This allows the determination of the child’s bone age, and based on the hands growth plates it can determined if the child is in their rapid phase of growth. Treatments include: Observation - For curves less than 20-25 degrees. This entails visits every 6-9 months with a repeat scoliosis x-ray. Since scoliosis curves increase only 1-2 degrees per month, and variations in measurements can be 3-5 degrees, an x-ray is not recommended before 6 months. If the curve remains less than 25 degrees the child is followed until their growth is completed (usually age 16-18). Progressing Curve - If growth is finished and the curve is less than 40 degrees, the risk of more curvature into adulthood is small. If growth is completed and the curve is over 45 degrees, the child is followed for several years as these curves can progress into adulthood. If the patient is still growing and the curve has progressed greater than 25 degrees but still in the non-operative range (less than 45-50 degrees) bracing is used to stop the progression of the curve. Bracing - Indicated for curves over 25 degrees but less than 45 degrees. If a brace is required you will be referred to an orthotist (bracing specialist). The orthotist assesses your child, reviews the x-ray and then fits the brace. (Having a brace made usually takes 2-3 weeks.) Once the brace is fit, your child will visit the scoliosis specialist for an x-ray in the brace to ensure it fits correctly. The primary goal of bracing is to halt progression of the curve and prevent the need for surgery. The brace must be worn for about 16 hours per day to be effective. In a recent bracing study 72% of the patients who wore their braces as prescribed prevented the need for surgery compared to the group who did not wear their brace. Surgery: When a curve reaches 45-50 degrees, and a child is still growing, surgery is usually recommended because the curve is likely to continue progress. If a curve is over 50 degrees and the child is done growing surgery also may be recommended. This is because when curves are over 50 degrees they tend to increase 1-2 degrees per year for the rest of your life. As curves get larger the amount of lung function tends to decrease which could cause breathing problems later in life. The goals of surgery are to stop the progression of the curve and safely correct any misalignment. This is accomplished by attaching implants (rods, screws, hooks and bands) to the spine. Bone graft is then placed around the implants to encourage the spine to fuse (grow together). This then forms a solid column of bone with metal rods in place, preventing the curve from changing. Most patients are back to their regular sports and activities six months post surgery.
-
Avoid Counterfeits and Find the Right Protective Mask with This Helpful Guide
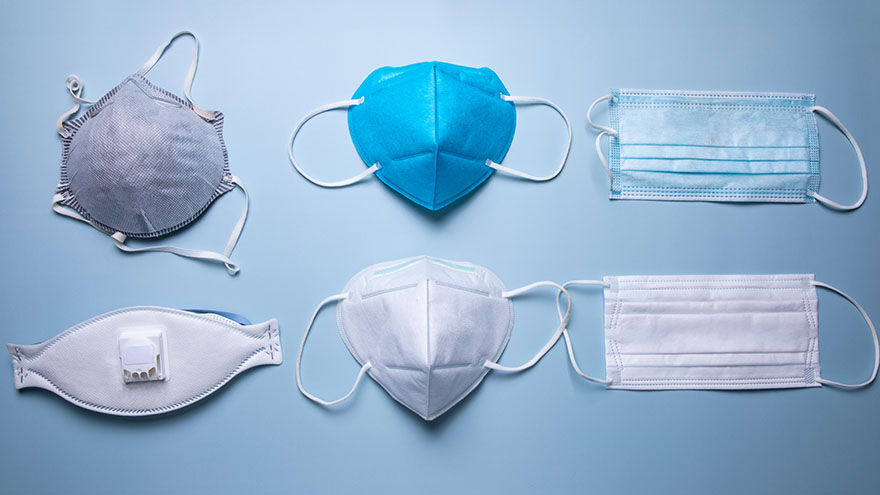
To better protect our patients, visitors and employees, cloth masks are no longer allowed at Renown facilities. Surgical masks, KN95 and N95 masks are allowed at Renown facilities. Appropriate face masks will be provided for visitors and patients who need one. With recent surges in the infectious COVID-19 omicron variant, many have sought to upgrade their face masks. But, let’s face it, shopping for face masks with adequate protection can be a challenge, especially considering the countless variations and the rise of counterfeit masks. Follow our straightforward guide below which includes some common red flags to help you discern between a high-quality face mask that provides proper protection and those that may be counterfeit. Types of Masks Qualities of a Real N95 Respirator Mask According to the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), N95 approved masks form a tight seal around your face and include a disposable respirator that removes particles including bacteria, viruses and dust as you breathe. N95 masks that are NIOSH approved undergo strict quality assurance and performance requirements to ensure mask respirators filter out up to 95% of hazardous particles. As a rule of thumb, N95 masks will not have ear loops, commonly used in cloth or surgical face masks. N95 respirators will contain two elastic bands or head straps that fasten behind the head, one securing the crown of the head and the other resting at the base of the neck, providing a snug fit and seal. Some other common signs that an N95 might be counterfeit include lack of all proper labeling, misspellings of NIOSH, decorative fabric and claiming to be approved for children. Currently, masks in adult sizes are the only masks to undergo NIOSH’s quality assurance and testing process. Respirators approved by NIOSH will include a testing certification (TC) approval number and will contain specific labeling on the facepiece of your mask. Find a full list of Center for Disease Control (CDC) and NIOSH requirements here. Identifying Real KN95 Respirator Masks Often preferred due to comfortability, the KN95 respirators were initially designed to meet Chinese standards for medical masks. Firstly, if a KN95 mask claims to be approved by the CDC, it is counterfeit as the CDC and NIOSH do not support any respiratory protective devices according to international standards. However, when KN95 masks are fitted and worn appropriately they do provide more protection than disposable masks. Legitimate KN95 masks will display a manufacturer number, GB2626-2019, ensuring accordance with current Chinese respirator standards for all masks made after July 1, 2021. Unlike N95 masks, it is important to note that KN95 masks are available in children's sizes. You might run into KN95 masks claiming to be “FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved” or “FDA-registered,” but be aware that this does not mean much and is a misleading statement. What this indicates is that a mask maker has submitted paperwork to the FDA, but the product has not been thoroughly tested for proper filtration and protection. Surgical Masks Medical procedure masks often referred to as surgical or disposable masks vary in their protection according to a variety of factors including fit and filtration. The CDC defines medical procedure masks as “variably shaped, including flat pleated, cone-shaped, or duck-bill. Medical procedure masks are loose and are not expected to provide a reliable level of protection against airborne or aerosolized particles as N95 respirators regulated by the National Institute of for Occupational Safety and Health.” However, these types of masks provide more protection than cloth masks and are certainly better than wearing no mask at all. Often popular due to their level of comfort and cost-effectiveness, surgical masks can be knotted in the ear loop areas to provide a tighter seal and can be layered for additional filtration. Depending upon your budget and level of comfortability and protection, one variation of mask may suit you over another. Please remember to do your part in limiting the spread of COVID-19 and wear a surgical mask, KN95 or N95 mask when visiting Renown facilities.
Read More About Avoid Counterfeits and Find the Right Protective Mask with This Helpful Guide